CBCT in Dentistry, accurate diagnosis and precision treatment planning are critical. Traditional 2D radiographs often fall short in delivering the level of detail needed for complex procedures. That’s where CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) steps in.
In this article, we’ll explore what CBCT is, when to use it, and why it’s becoming a must-have in dental practice.
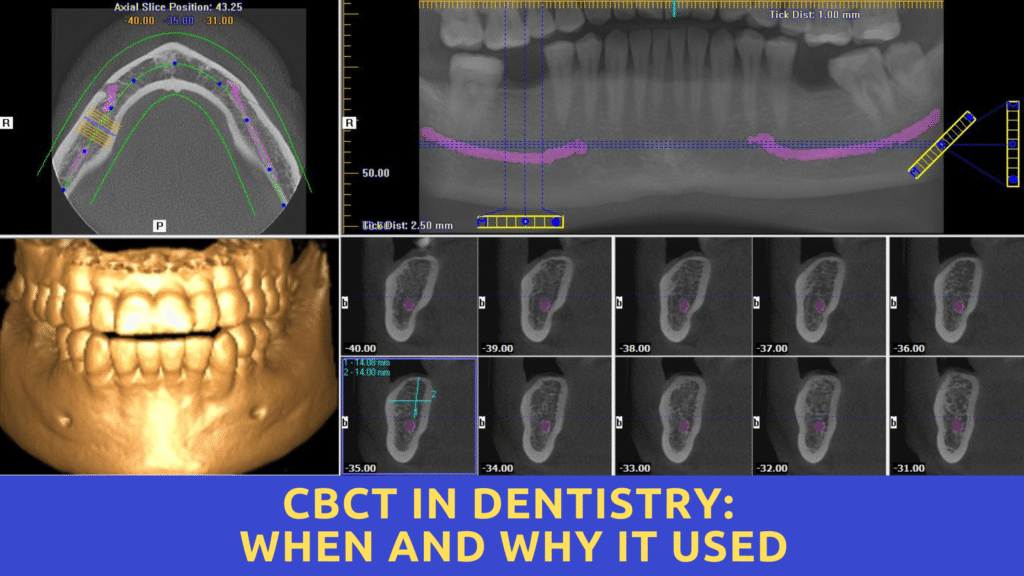
🧠 What is CBCT in Dentistry?
CBCT stands for Cone Beam Computed Tomography, a type of 3D imaging technology that provides a detailed view of teeth, bone, soft tissues, and nerve pathways in a single scan.
Unlike traditional X-rays, CBCT delivers volumetric images, making it highly valuable for diagnosis, surgical planning, and post-treatment assessment in various dental specialties.
✅ Why Use CBCT in Clinical Dentistry?
Here are key reasons to use CBCT in your dental practice:
1. Accurate 3D Imaging
CBCT scans produce detailed 3D images, allowing for more accurate diagnosis of root morphology, bone density, sinus anatomy, and impacted teeth.
2. Better Treatment Planning
It improves planning for:
- Dental implants
- Orthognathic surgeries
- Endodontic treatment
- Tooth impactions
- TMJ analysis
3. Minimally Invasive Diagnosis
Instead of exploratory surgery or uncertain guesswork, CBCT helps you see the unseen and reduce complications.
4. Time-Efficient & Comfortable
CBCT scans take just 10–40 seconds, with minimal discomfort for patients compared to traditional CT or multiple X-rays.
📅 When to Use CBCT in Dental Practice?
Here are the clinical situations where CBCT is recommended:
🦷 1. Implant Planning
- To evaluate bone width, height, and density
- To locate nerve canals and sinus floor
- To choose proper implant angulation and size
🔍 2. Endodontics
- Detection of extra canals, root fractures, and periapical lesions
- Retreatment cases where 2D X-rays are inconclusive
😬 3. Orthodontics
- Assessment of impacted teeth, root resorption, and skeletal relationships
- Better planning of orthodontic tooth movement
👃 4. Sinus and TMJ Evaluation
- Understanding maxillary sinus pathologies before surgery
- Assessing TMJ joint space, disc position, and bone morphology
👄 5. Oral Pathology and Lesion Evaluation
- Accurate sizing and localization of cysts, tumors, or abnormal growths
🦴 6. Trauma Cases
- For fracture detection, displacement, or foreign body localization
⚠️ Limitations of CBCT
While CBCT is a powerful tool, it’s not without its limitations:
- Higher radiation dose than intraoral X-rays (though much lower than medical CT)
- Artifacts in images if the patient moves
- Not ideal for soft tissue imaging (e.g., tongue, muscles)
💡 Conclusion: Should You Invest in CBCT?
CBCT is rapidly becoming an essential diagnostic tool in implantology, endodontics, oral surgery, orthodontics, and TMJ analysis. While it involves an investment, the diagnostic accuracy, treatment precision, and patient trust it brings are often worth it.
If you’re serious about offering modern, evidence-based dental care, CBCT could be a game-changer for your practice.
